- Published on
What Is Crohn's Disease?
- Authors
- Name
- Jake Konigsberg
- Role
- Founder
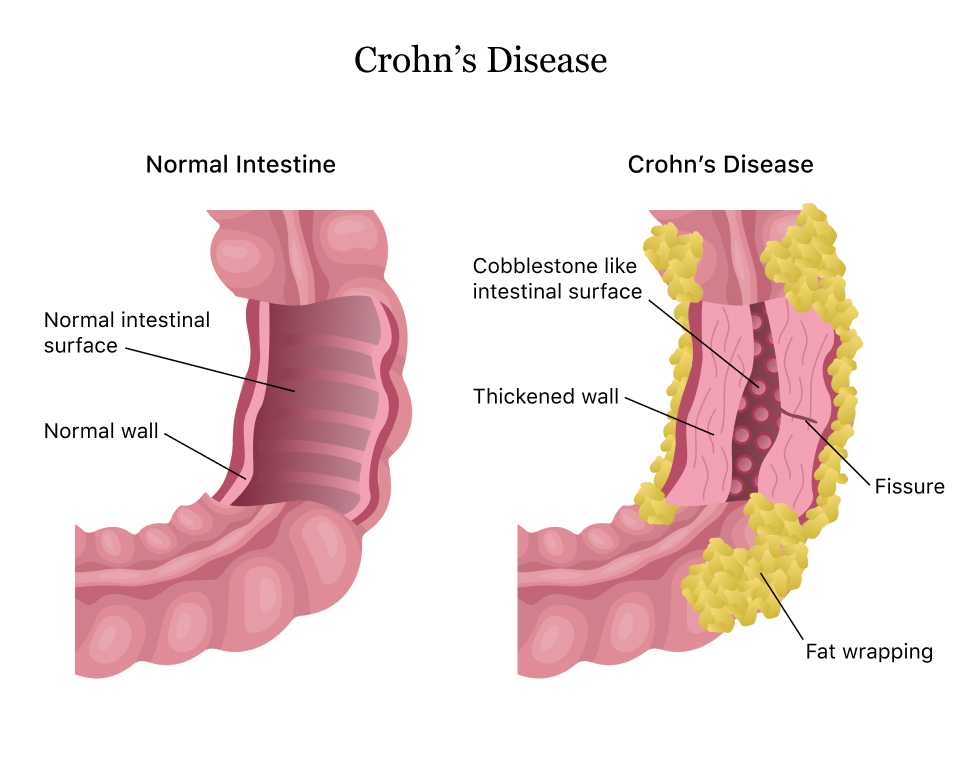
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory disease that causes inflammation throughout the gastrointestinal tract. In other words, when one has Crohn's disease, the immune system is attacking the body’s tissue in the gastrointestinal tract (the passageway of the digestive system beginning at the mouth and ending at the anus) resulting in swelling. The inflammation that is characteristic of Crohn’s disease can occur anywhere throughout the gastrointestinal tract with the most common location of inflammation being the small intestine. The effects of Crohn’s disease can even extend beyond the gastrointestinal tract to other organs like the eyes and skin. Crohn’s disease is chronic but treatments can reduce its symptoms and effects and even bring about remission.
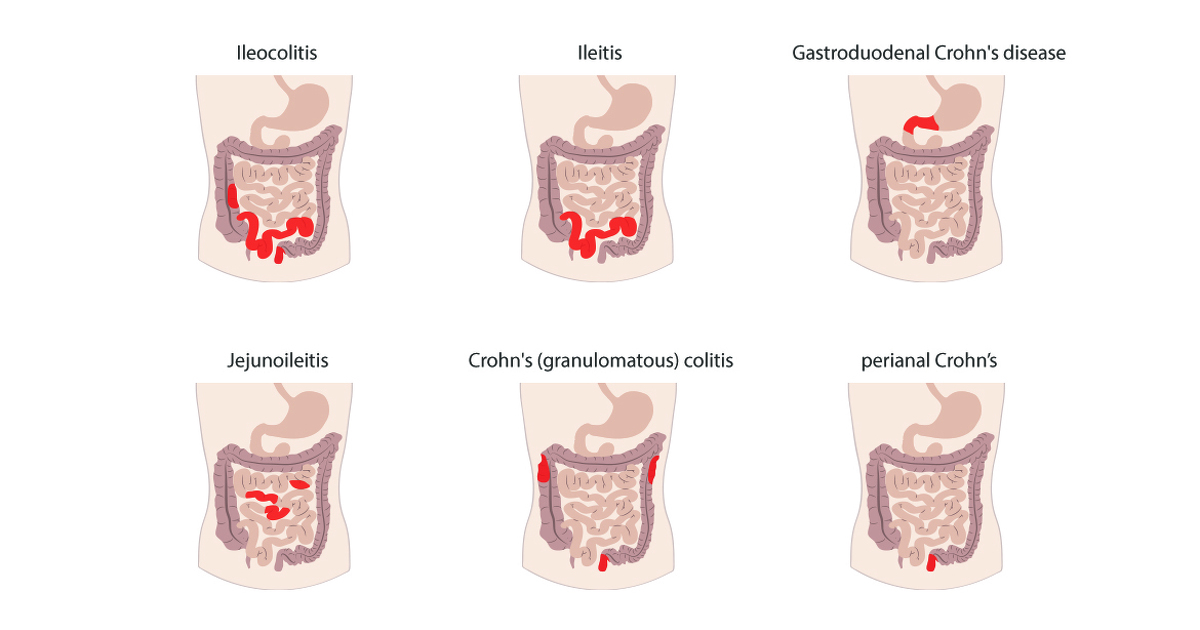
There are various types of Crohn’s disease categorized based on where the inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract occurs; here are the main types:
- Ileocolitis– Inflammation of the colon (the longest part of the large intestine) and the ileum (the last part of the small intestine) and caused by Crohn’s disease. Ileocolitis is the most common form of Crohn’s disease.
- Ileitis– Inflammation of only the ileum and may be caused by Crohn’s disease but could also be caused by other inflammatory diseases.
- Gastroduodenal Crohn’s– Inflammation of the stomach and duodenum (the beginning of the small intestine) and is caused by Crohn’s disease.
- Jejunoileitis– Inflammation of the jejunum (the upper half of the small intestine) and is caused by Crohn’s disease.
- Crohn’s (Granulomatous) Colitis– Inflammation of only the colon and is caused by Crohn’s disease
The exact cause of Crohn’s disease is unknown; however, there are many factors that are suspected to play a role in its development. One possible factor is that the body’s immune system views harmless microorganisms like bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract as foreign invaders which would result in the immune system attacking the tissue of the. gastrointestinal tract. Another possible factor is genetics. While most people who develop Crohn’s disease have no family history of it, those who have a family history of it have been shown to have an elevated risk of developing the disease, suggesting that genes likely play a role. There are various other factors that may increase the severity or risk of developing the disease like environment, stress, and diet.