- Published on
Diabetes-- Signs, Stats, and Facts
- Authors
- Name
- Magdeline Gomes
- Role
- Content Writer
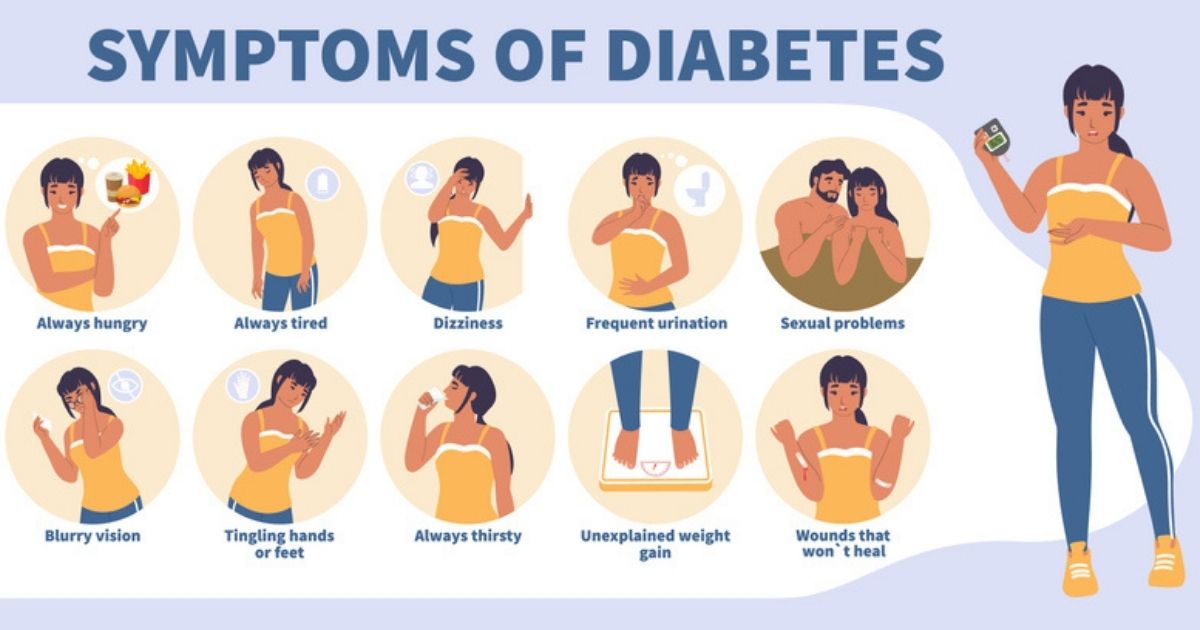
The signs associated with diabetes are correlated with how high your blood sugar is ― this can result in individuals not knowing if they have prediabetes or type 2 diabetes due to a lack of signs.
Signs to look out for (both type 1 and type 2):
Unusual thirst
Urinating often
Effortless weight loss
Presence of ketones (a byproduct of the breakdown of muscle and fat that occurs when there's not enough available insulin) in the urine
Fatigue
Unusual mood changes
Increased rate of infections (such as skin infections)
Approximately 537 million adults (20-79 years) are living with diabetes. Even more alarming is that the total number of people living with diabetes is projected to rise to 643 million by 2030 and 783 million by 2045. Diabetes can be deadly and is a leading cause of death with it directly responsible for 1.5 million fatalities annually. Globally, 21 million (or 1 in 6) women are affected by diabetes during pregnancy with what it is known as gestational diabetes. In the United States, 96 million adults—more than 1 in 3 of all adults—have prediabetes (elevated blood sugar levels). Around 80% of individuals with prediabetes don’t know that they have the condition which is particularly dangerous as then they don't know they need to change their behavior to avoid the development of type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is much more prevalent in adults compared to type 1 diabetes. In fact, around 90-95% of diabetes cases in adults are due to type 2 diabetes. Nevertheless, nearly 1.9 million Americans still suffer from type 1 diabetes. This statistic includes around 244,000 children and adolescents. These numbers are still increasing heavily each year, with 1.4 million Americans being diagnosed on average per year.
Despite common belief, eating sugar doesn't cause diabetes. This misunderstanding may come from the confusion regarding glucose production from the foods you consume. Insulin, the hormone impacted by diabetes, moves glucose into cells. The problem boils down to diabetes sufferers having a problem regarding ineffective insulin instead of the amount of sugary content consumed. Although, this doesn’t mean you can eat all the sugar to your heart’s content ― eating too much sugar can cause you to become overweight, which heightens the risk of diabetes.
