- Published on
Diabetes Treatment: Insulin Therapy
- Authors
- Name
- Magdeline Gomes
- Role
- Content Writer
- Name
- Jake Konigsberg
- Role
- Founder
Insulin is a hormone that is produced by the pancreas. Insulin helps the body store and use glucose, the main energy source for the body. In patients with diabetes, there is a lack of insulin which results in glucose not entering cells, preventing the body from using glucose for energy and causing high blood glucose levels. Insulin therapy aims to replace the insulin that is missing from the body to lower blood sugar levels and minimize long-term consequences.
Although insulin therapy comes in a variety of forms, they all have the same goal which is to regulate blood sugar levels and bring them down to a healthy point. The difference is simply how long the effects last. It's up to a diabetes sufferer's needs to determine what prescription is required.
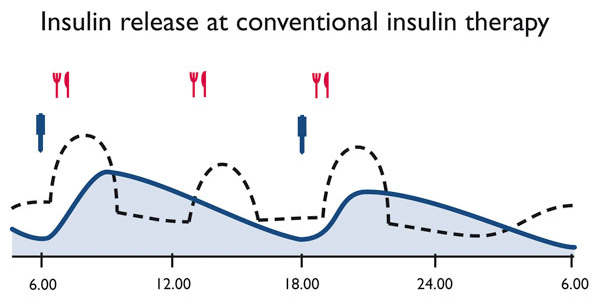
Conventional insulin therapy involves an injection of insulin twice a day. This treatment plan is often chosen by sufferers who have a regular routine as it allows them to inject their insulin at the same times every day. The majority of people inject a combination of both short-acting and long-acting insulin. They take this mixture twice a day, once before breakfast and once before dinner. They must eat set portions of food on a regular basis throughout the day to offset the effects of insulin. This method is less effective for those who suffer from type 1 diabetes.
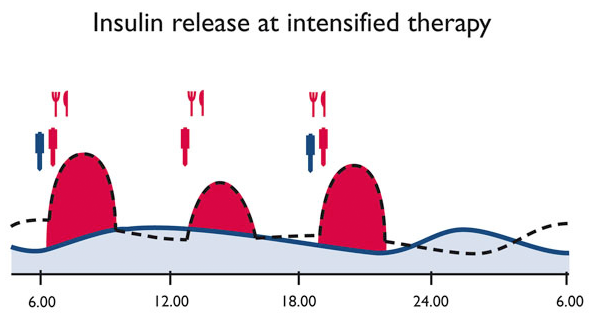
Intensive insulin therapy is the name for the alternative technique. Based on a person's blood sugar levels, how much they eat, and how active they are, the amount of insulin can be changed flexibly and spontaneously. Here, it's crucial to regularly monitor blood sugar levels. You can provide daily injections of insulin either manually or with an insulin pump. Longer-acting insulin is administered once or twice per day to meet daily insulin requirements. This administration of longer-acting insulin is frequently called "basal insulin." Before every meal, short-acting insulin is also administered to help the body metabolize the carbohydrates in the meals. This administration is commonly referred to as a "bolus dose". The benefit of this approach, as opposed to conventional insulin therapy, is that it assists in reducing the chance of developing diabetes-related complications, including those that impact the nervous system, eyes, and kidneys.
Additional treatments that benefit those suffering from diabetes include eating healthy and exercising. In terms of eating healthy, it is recommended one cuts down on saturated fats, refined carbohydrates, and sweets. Exercising is also helpful as it lowers blood sugar levels, as during exercise, the sugar is being used for energy, causing it to be transported into cells.